Wikijunior:The Elements/Barium
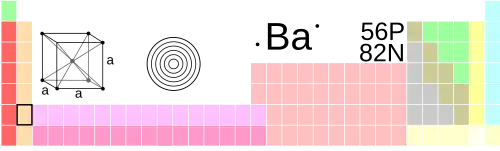

Barium is classified as an alkaline earth metal on the periodic table. The periodic table arranges chemical elements into periods (rows) and groups (columns). The element barium is in period 6 and group 2. Its atomic number is 56 and its symbol is Ba.
In addition to barium, there are 5 other alkaline earth metals: beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, and radium. These elements have similar properties. They are highly reactive and form useful compounds.

What does it look, feel, taste, or smell like?
Barium is a soft, silvery-white metal. When exposed to air, a dark gray coating appears on its surface. This process is called oxidation. Barium is typically stored in high-purity mineral oil or paraffin oil. These oils provide a protective barrier against oxidation by air or water.
In its pure metallic form, barium has no odor. It is highly toxic and should never be tasted. The compound barium sulfide has a “rotten egg” smell when exposed to moisture. This compound is highly toxic. The compound barium sulfate is non-toxic and safely used by doctors for medical imaging.
How was it discovered?
A shoemaker named Vincentius Casciorolus learned about the heavy, silvery-white mineral which was impure barium sulfate (BaS04). He noticed that after being heated up, this mineral would change into unusual pebbles that glowed for years. He named these pebbles "Bologna stones", and they were later determined to be barium sulfate. Then, barium was first discovered in barite by German chemist Carl Scheele and English chemist William Withering in the late 18th century.
In 1772, Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele was experimenting with various compounds. He did not discover barium as a distinct element.
In 1808, English chemist Sir Humphry Davy isolated barium metal. He passed an electric current through molten barium chloride. This method is known as “electrolysis”.
Where did its name come from?
The name barium comes from the Greek word βαρὺς (barys), meaning "heavy." Sir Humphry Davy officially named the new element barium. The -ium suffix indicates a metallic element.
Where did its name come from?
The name barium comes from the Greek word βαρὺς (barys), meaning "heavy." Sir Humphry Davy officially named the new element barium. The -ium suffix indicates a metallic element.
Did You Know?
- Hydrogen gas is released when barium reacts exothermically with water.
- Barium makes up only 0.0425% of the Earth’s crust.
- Breathing in pure barium can irritate the lungs.
- Barium creates a dark gray coating when it is oxidized in air.
- Barium is commonly alloyed with metals such as aluminum.
Where is it found?
Barium has a high chemical reactivity. As such, it is never found naturally in its pure form. In nature, it reacts with water to form barium hydroxide, and oxygen to form barium oxide.
Barium is found in barite and witherite. Barium is mined in China, India, Germany, and Morocco. In the United States, it is mined in Alabama, Alaska, Arizona and Arkansas.
What are its uses?
Barium is used to color fireworks green. It can also be used to help create a vacuum in television tubes by removing unwanted gas from the tube. Barium compounds are used in various industries including electronics, ceramics, paints, oil and gas. In medicine, barium sulfate is used in contrast imaging to help doctors see inside the body.
Is it dangerous?
Barium is very toxic in its elemental form. A very small amount can be deadly. The compounds barium chloride and barium nitrate are highly toxic. Swallowing or inhaling these compounds can lead to muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, and paralysis.
References
Britannica Kids. (2025). Barium – Students | Britannica Kids | Homework Help. https://kids.britannica.com
Kiddle Encyclopedia. (2025, April 15). Barium facts for kids. https://kids.kiddle.co/Barium
Persson Rare Minerals. (2020). Witherite: Pigeon Roost mine, Glenwood, Montgomery Co., Arkansas USA. https://perssonrareminerals.com/?product=witherite-pigeon-roost-mine-glenwood-montgomery-co-arkansas-usa
SchoolMyKids. (n.d.). Barium (Ba) – Atomic, physical & chemical properties, uses, and periodic table trends. https://www.schoolmykids.com/
Sedawie, R. (2023). Witherite gemstone: Properties, meanings, value & more. https://www.gemrockauctions.com/learn/a-z-of-gemstones/witherite
University of Nottingham. (n.d.). Barium – Periodic Table of Videos [Video].