Here is a little class that uses the Bose-Nelson algorithm to generate a sorting network on compile time.
/**
* A Functor class to create a sort for fixed sized arrays/containers with a
* compile time generated Bose-Nelson sorting network.
* \tparam NumElements The number of elements in the array or container to sort.
* \tparam T The element type.
* \tparam Compare A comparator functor class that returns true if lhs < rhs.
*/
template <unsigned NumElements, class Compare = void> class StaticSort
{
template <class A, class C> struct Swap
{
template <class T> inline void s(T &v0, T &v1)
{
T t = Compare()(v0, v1) ? v0 : v1; // Min
v1 = Compare()(v0, v1) ? v1 : v0; // Max
v0 = t;
}
inline Swap(A &a, const int &i0, const int &i1) { s(a[i0], a[i1]); }
};
template <class A> struct Swap <A, void>
{
template <class T> inline void s(T &v0, T &v1)
{
// Explicitly code out the Min and Max to nudge the compiler
// to generate branchless code.
T t = v0 < v1 ? v0 : v1; // Min
v1 = v0 < v1 ? v1 : v0; // Max
v0 = t;
}
inline Swap(A &a, const int &i0, const int &i1) { s(a[i0], a[i1]); }
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int J, int X, int Y> struct PB
{
inline PB(A &a)
{
enum { L = X >> 1, M = (X & 1 ? Y : Y + 1) >> 1, IAddL = I + L, XSubL = X - L };
PB<A, C, I, J, L, M> p0(a);
PB<A, C, IAddL, J + M, XSubL, Y - M> p1(a);
PB<A, C, IAddL, J, XSubL, M> p2(a);
}
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int J> struct PB <A, C, I, J, 1, 1>
{
inline PB(A &a) { Swap<A, C> s(a, I - 1, J - 1); }
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int J> struct PB <A, C, I, J, 1, 2>
{
inline PB(A &a) { Swap<A, C> s0(a, I - 1, J); Swap<A, C> s1(a, I - 1, J - 1); }
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int J> struct PB <A, C, I, J, 2, 1>
{
inline PB(A &a) { Swap<A, C> s0(a, I - 1, J - 1); Swap<A, C> s1(a, I, J - 1); }
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int M, bool Stop = false> struct PS
{
inline PS(A &a)
{
enum { L = M >> 1, IAddL = I + L, MSubL = M - L};
PS<A, C, I, L, (L <= 1)> ps0(a);
PS<A, C, IAddL, MSubL, (MSubL <= 1)> ps1(a);
PB<A, C, I, IAddL, L, MSubL> pb(a);
}
};
template <class A, class C, int I, int M> struct PS <A, C, I, M, true>
{
inline PS(A &a) {}
};
public:
/**
* Sorts the array/container arr.
* \param arr The array/container to be sorted.
*/
template <class Container> inline void operator() (Container &arr) const
{
PS<Container, Compare, 1, NumElements, (NumElements <= 1)> ps(arr);
};
/**
* Sorts the array arr.
* \param arr The array to be sorted.
*/
template <class T> inline void operator() (T *arr) const
{
PS<T*, Compare, 1, NumElements, (NumElements <= 1)> ps(arr);
};
};
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
enum { NumValues = 32 };
// Arrays
{
int rands[NumValues];
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) rands[i] = rand() % 100;
std::cout << "Before Sort: \t";
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) std::cout << rands[i] << " ";
std::cout << "\n";
StaticSort<NumValues> staticSort;
staticSort(rands);
std::cout << "After Sort: \t";
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) std::cout << rands[i] << " ";
std::cout << "\n";
}
std::cout << "\n";
// STL Vector
{
std::vector<int> rands(NumValues);
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) rands[i] = rand() % 100;
std::cout << "Before Sort: \t";
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) std::cout << rands[i] << " ";
std::cout << "\n";
StaticSort<NumValues> staticSort;
staticSort(rands);
std::cout << "After Sort: \t";
for (int i = 0; i < NumValues; ++i) std::cout << rands[i] << " ";
std::cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
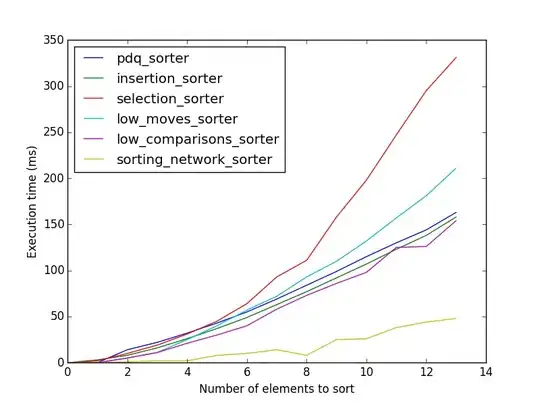
Benchmarks
The following benchmarks are compiled with clang -O3 and ran on my mid-2012 macbook air.
Time (in milliseconds) to sort 1 million arrays.
The number of milliseconds for arrays of size 2, 4, 8 are 1.943, 8.655, 20.246 respectively.

Here are the average clocks per sort for small arrays of 6 elements. The benchmark code and examples can be found at this question:
Fastest sort of fixed length 6 int array
Direct call to qsort library function : 342.26
Naive implementation (insertion sort) : 136.76
Insertion Sort (Daniel Stutzbach) : 101.37
Insertion Sort Unrolled : 110.27
Rank Order : 90.88
Rank Order with registers : 90.29
Sorting Networks (Daniel Stutzbach) : 93.66
Sorting Networks (Paul R) : 31.54
Sorting Networks 12 with Fast Swap : 32.06
Sorting Networks 12 reordered Swap : 29.74
Reordered Sorting Network w/ fast swap : 25.28
Templated Sorting Network (this class) : 25.01
It performs as fast as the fastest example in the question for 6 elements.
The code used for the benchmarks can be found here.
It includes more features and further optimizations for more robust performance on real-world data.