There are three fast ways to read multiple files and put them into a single data frame or data table
First get the list of all txt files (including those in sub-folders)
list_of_files <- list.files(path = ".", recursive = TRUE,
pattern = "\\.txt$",
full.names = TRUE)
1) Use fread() w/ rbindlist() from the data.table package
#install.packages("data.table", repos = "https://cran.rstudio.com")
library(data.table)
# Read all the files and create a FileName column to store filenames
DT <- rbindlist(sapply(list_of_files, fread, simplify = FALSE),
use.names = TRUE, idcol = "FileName")
2) Use readr::read_table2() w/ purrr::map_df() from the tidyverse framework:
#install.packages("tidyverse",
# dependencies = TRUE, repos = "https://cran.rstudio.com")
library(tidyverse)
# Read all the files and create a FileName column to store filenames
df <- list_of_files %>%
set_names(.) %>%
map_df(read_table2, .id = "FileName")
3) (Probably the fastest out of the three) Use vroom::vroom():
#install.packages("vroom",
# dependencies = TRUE, repos = "https://cran.rstudio.com")
library(vroom)
# Read all the files and create a FileName column to store filenames
df <- vroom(list_of_files, .id = "FileName")
Note: to clean up file names, use basename or gsub functions
Benchmark: readr vs data.table vs vroom for big data
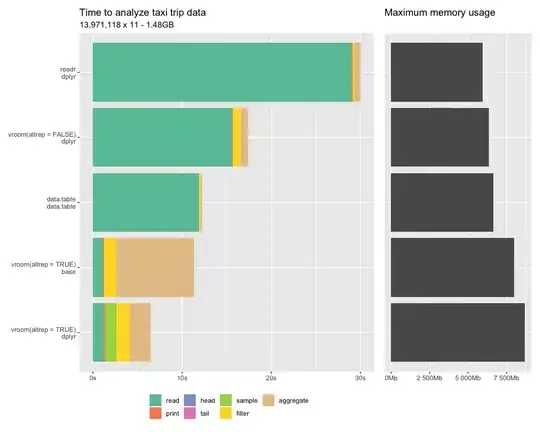
Edit 1: to read multiple csv files and skip the header using readr::read_csv
list_of_files <- list.files(path = ".", recursive = TRUE,
pattern = "\\.csv$",
full.names = TRUE)
df <- list_of_files %>%
purrr::set_names(nm = (basename(.) %>% tools::file_path_sans_ext())) %>%
purrr::map_df(read_csv,
col_names = FALSE,
skip = 1,
.id = "FileName")
Edit 2: to convert a pattern including a wildcard into the equivalent regular expression, use glob2rx()
