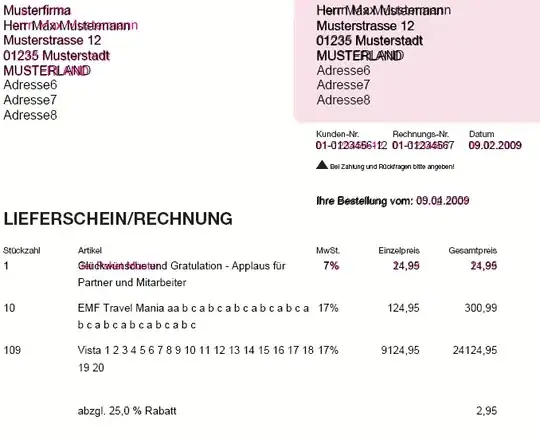
In case the binwidth is fixed, here is an alternative solution which is using the internal function ggplot2:::bin_breaks_width() to get the number of bins before creating the graph. It's still a workaround but avoids to call geom_histogram() twice as in the other solution:
# create sample data
set.seed(1L)
myData <- abs(rnorm(1000))
binwidth <- 0.1
# create plot
library(ggplot2) # CRAN version 2.2.1 used
n_bins <- length(ggplot2:::bin_breaks_width(range(myData), width = binwidth)$breaks) - 1L
ggplot() + geom_histogram(aes(x = myData), binwidth = binwidth, fill = rainbow(n_bins))
As a third alternative, the aggregation can be done outside of ggplot2. Then, geom_col() cam be used instead of geom_histogram():
# start binning on multiple of binwidth
start_bin <- binwidth * floor(min(myData) / binwidth)
# compute breaks and bin the data
breaks <- seq(start_bin, max(myData) + binwidth, by = binwidth)
myData2 <- cut(sort(myData), breaks = breaks, by = binwidth)
ggplot() + geom_col(aes(x = head(breaks, -1L),
y = as.integer(table(myData2)),
fill = levels(myData2))) +
ylab("count") + xlab("myData")
Note that breaks is plotted on the x-axis instead of levels(myData2) to keep the x-axis continuous. Otherwise each factor label would be plotted which would clutter the x-axis. Also note that the built-in ggplot2 color palette is used instead of rainbow().