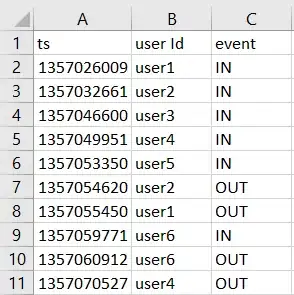
In response to your question in the comment about reading the file, something like below:
Note that I am using early-binding (set reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime), but you could also use late binding, especially if the code will be distributed.
Dim V
Dim fn As Variant
Dim FSO As FileSystemObject, TS As TextStream
fn = Application.GetOpenFilename("CSV Files(*.csv),*.csv")
If fn = False Then Exit Sub
Set FSO = New FileSystemObject
Set TS = FSO.OpenTextFile(fn, ForReading, False, TristateUseDefault)
V = Split(TS.ReadAll, vbNewLine)
V will now contain a zero-based array where each element consists of one line/row from the csv file.
Edit
In response to your question about storing the information in the Dictionary object, if you change your code to:
If Not dict.Exists(elements(1)) Then
Set collec = New Collection
collec.Add elements(0)
dict.Add (elements(1)), collec
Else
dict(elements(1)).Add elements(0)
End If
will store the time stamps associated with each userID.
If you assume that every user has an IN, and that there is an OUT for every IN then you can just go through sequentially. But you'd be better off checking, and also storing the event type with the time, so as to avoid errors. Or storing the ts's in pairs (arrays) with the first element being IN and the second being OUT. pre-Sorting the data by USER ID, and then by TS, might be helpful as you would only need to check the line below for equality of user id, and an OUT event (after each IN event).
Edit2
I think the following will do what you want.
Although not necessary, I am using a class module as it makes documentation and modifications much simpler.
Here is the algorithm:
- Read the entire CSV file into a variant array
- Split on the newline character
- Write to a temporary worksheet
- sort on User ID, then on Time
- This should result in sequential IN/OUT if both exist
- Could write a VBA sort routine, but I don't happen to have a fast, "stable" one, and the Excel sorting is pretty flexible, as well as being stable and fast.
- With the sorted order, create a dictionary where the Key is a generated sequential number, and the item is a class object consisting of the User ID, TS IN and TS OUT
- have to check the next line to be sure there is an OUT that matches the IN for that user, otherwise, don't add it to the dictionary.
- Create results worksheets - one for all the data, and one for each month.
- Write the results to the results worksheet. Include a column for the monthIN (see the Class module for that calculation)
- Filter the results to populate the Months worksheets
Class Module
'**RENAME**: cUser
Option Explicit
Private puserID As String
Private ptmIN As Long
Private ptmOUT As Long
Public Property Get userID() As String
userID = puserID
End Property
Public Property Let userID(value As String)
puserID = value
End Property
Public Property Get tmIN()
If ptmIN = 0 Then
tmIN = ""
Else
tmIN = ptmIN
End If
End Property
Public Property Let tmIN(value)
ptmIN = value
End Property
Public Property Get tmOUT()
If ptmOUT = 0 Then
tmOUT = ""
Else
tmOUT = ptmOUT
End If
End Property
Public Property Let tmOUT(value)
ptmOUT = value
End Property
Public Property Get monthIN() As Long
monthIN = Month(DateAdd("s", Me.tmIN, DateSerial(1970, 1, 1)))
End Property
Public Property Get monthOUT() As Long
monthOUT = Month(DateAdd("s", Me.tmOUT, DateSerial(1970, 1, 1)))
End Property
Regular Module
Option Explicit
Sub inOUT()
Dim FSO As FileSystemObject, TS As TextStream
Dim dU As Dictionary, cU As cUser
Dim fn As Variant
Dim vSrc, vRes, V
Dim I As Long, J As Long
Dim sKey As String
Dim wb As Workbook, ws As Worksheet, r As Range
Dim wsRes As Worksheet, wsMonth(1 To 12) As Worksheet, rMonth As Range
Dim eventID As Long
'Read file
fn = Application.GetOpenFilename("Text File (*.txt;*.csv), *.txt;*.csv")
If fn = False Then Exit Sub
Set FSO = New FileSystemObject
Set TS = FSO.OpenTextFile(fn, ForReading, False, TristateUseDefault)
vSrc = Split(TS.ReadAll, vbNewLine) ' line = one array element
'write to temp worksheet
'split text to columns
'sort by user id, then by time
'read back into array
'delete the temp worksheet
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Set ws = Worksheets.Add
Set r = ws.Cells(1, 1).Resize(UBound(vSrc) + 1)
r = WorksheetFunction.Transpose(vSrc)
r.TextToColumns DataType:=xlDelimited, textqualifier:=xlTextQualifierDoubleQuote, consecutivedelimiter:=True, _
Tab:=False, semicolon:=False, comma:=True, Space:=False, other:=False
Set r = r.CurrentRegion
r.Sort key1:=r.Columns(2), order1:=xlAscending, key2:=r.Columns(1), order2:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes, MatchCase:=False
vSrc = r
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
ws.Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
'collect into dictionary
'assign sequential event ID's
'new event ID for every `IN` event
'same event ID if Next line is an `OUT` and `user id` matches
eventID = 0
Set dU = New Dictionary
For I = 2 To UBound(vSrc, 1) 'skip header line
If IsNumeric(vSrc(I, 1)) Then
eventID = eventID + 1
Set cU = New cUser
With cU
.userID = vSrc(I, 2)
If vSrc(I, 3) = "IN" Then .tmIN = vSrc(I, 1)
If vSrc(I + 1, 3) = "OUT" And vSrc(I + 1, 2) = .userID Then
.tmOUT = vSrc(I + 1, 1)
I = I + 1
'add to dictionary
dU.Add Key:=eventID, Item:=cU
End If
End With
End If
Next I
'create results array
ReDim vRes(0 To dU.Count, 1 To 5)
'headers
vRes(0, 1) = "Event ID"
vRes(0, 2) = "User ID"
vRes(0, 3) = "TS IN"
vRes(0, 4) = "TS OUT"
vRes(0, 5) = "Month IN"
'Data
I = 0
For Each V In dU.Keys
I = I + 1
Set cU = dU(V)
With cU
If (.tmOUT - .tmIN) < (86400 * 48) And _
.monthIN = .monthOUT Then
vRes(I, 1) = V
vRes(I, 2) = .userID
vRes(I, 3) = .tmIN
vRes(I, 4) = .tmOUT
vRes(I, 5) = .monthIN
End If
End With
Next V
'set results worksheets
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
On Error Resume Next
For J = 1 To 12
Set wsMonth(J) = Worksheets(MonthName(J))
If Err.Number = 9 Then
Set wsMonth(J) = Worksheets.Add
wsMonth(J).Name = MonthName(J)
End If
wsMonth(J).Cells.Clear
Next J
Set wsRes = Worksheets("Results")
If Err.Number = 9 Then
Set wsRes = Worksheets.Add
wsRes.Name = "Results"
End If
On Error GoTo 0
'write and sort all the results
Set r = wsRes.Cells(1, 1).Resize(UBound(vRes, 1) + 1, UBound(vRes, 2))
With r
.EntireColumn.Clear
.value = vRes
.Range(.Columns(3), .Columns(4)).NumberFormat = "#"
.Sort key1:=r.Columns(3), order1:=xlAscending, Header:=xlYes
.Style = "Output"
.EntireColumn.AutoFit
'Filter to the month sheets
For J = 1 To 12
.AutoFilter Field:=5, Criteria1:=J
.Resize(columnsize:=4).SpecialCells(xlCellTypeVisible).Copy wsMonth(J).Cells(1, 1)
wsMonth(J).UsedRange.EntireColumn.AutoFit
Next J
End With
r.AutoFilter
End Sub
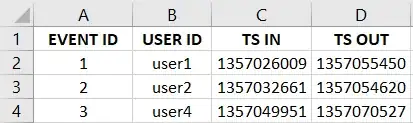
Here are the results on the January worksheet:
For as long as it is available, an excellent reference for basic information about classes can be found at the late Chip Pearson's website page Introduction to Classes