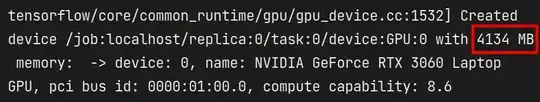
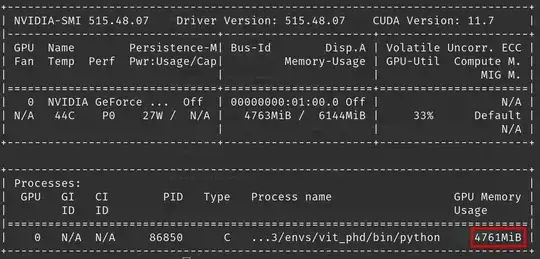
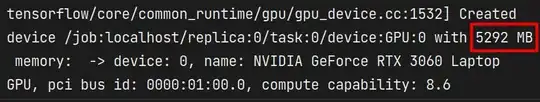
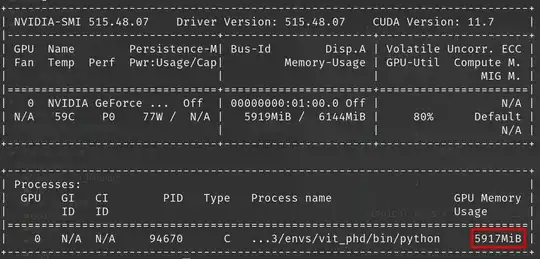
I have a laptop that has an RTX 2060 GPU and I am using Keras and TF 2 to train an LSTM on it. I am also monitoring the gpu use by nvidia-smi and I noticed that the jupyter notebook and TF are using maximum 35% and usually the gpu is being used between 10-25%.
With current conditions, it took more than 7 hours to train this model, I want to know if I am doing something wrong or it is a limitation of Keras and TF?
My nvidia-smi output:
Sun Nov 3 00:07:37 2019
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 430.26 Driver Version: 430.26 CUDA Version: 10.2 |
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|===============================+======================+======================|
| 0 GeForce RTX 2060 Off | 00000000:01:00.0 On | N/A |
| N/A 51C P3 22W / N/A | 834MiB / 5931MiB | 24% Default |
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: GPU Memory |
| GPU PID Type Process name Usage |
|=============================================================================|
| 0 1032 G /usr/lib/xorg/Xorg 330MiB |
| 0 1251 G /usr/bin/gnome-shell 333MiB |
| 0 1758 G ...equest-channel-token=622209288718607755 121MiB |
| 0 5086 G ...uest-channel-token=12207632792533837012 47MiB |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
My LSTM:
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout
regressor = Sequential()
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180, return_sequences = True, input_shape = (X_train.shape[1], 3)))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180, return_sequences = True))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180, return_sequences = True))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180, return_sequences = True))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180, return_sequences = True))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(LSTM(units = 180))
regressor.add(Dropout(0.2))
regressor.add(Dense(units = 1))
regressor.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'mean_squared_error')
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs = 10, batch_size = 32, callbacks=[cp_callback])