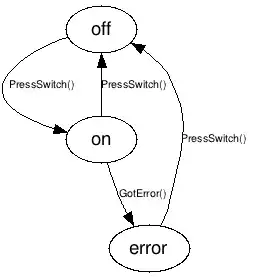
I've just contributed this:
https://code.google.com/p/ysharp/source/browse/#svn%2Ftrunk%2FStateMachinesPoC
Here's one of the examples demoing direct and indirect sending of commands, with states as IObserver(of signal), thus responders to a signal source, IObservable(of signal):
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
using Machines;
public static class WatchingTvSampleAdvanced
{
// Enum type for the transition triggers (instead of System.String) :
public enum TvOperation { Plug, SwitchOn, SwitchOff, Unplug, Dispose }
// The state machine class type is also used as the type for its possible states constants :
public class Television : NamedState<Television, TvOperation, DateTime>
{
// Declare all the possible states constants :
public static readonly Television Unplugged = new Television("(Unplugged TV)");
public static readonly Television Off = new Television("(TV Off)");
public static readonly Television On = new Television("(TV On)");
public static readonly Television Disposed = new Television("(Disposed TV)");
// For convenience, enter the default start state when the parameterless constructor executes :
public Television() : this(Television.Unplugged) { }
// To create a state machine instance, with a given start state :
private Television(Television value) : this(null, value) { }
// To create a possible state constant :
private Television(string moniker) : this(moniker, null) { }
private Television(string moniker, Television value)
{
if (moniker == null)
{
// Build the state graph programmatically
// (instead of declaratively via custom attributes) :
Handler<Television, TvOperation, DateTime> stateChangeHandler = StateChange;
Build
(
new[]
{
new { From = Television.Unplugged, When = TvOperation.Plug, Goto = Television.Off, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.Unplugged, When = TvOperation.Dispose, Goto = Television.Disposed, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.Off, When = TvOperation.SwitchOn, Goto = Television.On, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.Off, When = TvOperation.Unplug, Goto = Television.Unplugged, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.Off, When = TvOperation.Dispose, Goto = Television.Disposed, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.On, When = TvOperation.SwitchOff, Goto = Television.Off, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.On, When = TvOperation.Unplug, Goto = Television.Unplugged, With = stateChangeHandler },
new { From = Television.On, When = TvOperation.Dispose, Goto = Television.Disposed, With = stateChangeHandler }
},
false
);
}
else
// Name the state constant :
Moniker = moniker;
Start(value ?? this);
}
// Because the states' value domain is a reference type, disallow the null value for any start state value :
protected override void OnStart(Television value)
{
if (value == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("value", "cannot be null");
}
// When reaching a final state, unsubscribe from all the signal source(s), if any :
protected override void OnComplete(bool stateComplete)
{
// Holds during all transitions into a final state
// (i.e., stateComplete implies IsFinal) :
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(!stateComplete || IsFinal);
if (stateComplete)
UnsubscribeFromAll();
}
// Executed before and after every state transition :
private void StateChange(IState<Television> state, ExecutionStep step, Television value, TvOperation info, DateTime args)
{
// Holds during all possible transitions defined in the state graph
// (i.e., (step equals ExecutionStep.LeaveState) implies (not state.IsFinal))
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert((step != ExecutionStep.LeaveState) || !state.IsFinal);
// Holds in instance (i.e., non-static) transition handlers like this one :
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(this == state);
switch (step)
{
case ExecutionStep.LeaveState:
var timeStamp = ((args != default(DateTime)) ? String.Format("\t\t(@ {0})", args) : String.Empty);
Console.WriteLine();
// 'value' is the state value that we are transitioning TO :
Console.WriteLine("\tLeave :\t{0} -- {1} -> {2}{3}", this, info, value, timeStamp);
break;
case ExecutionStep.EnterState:
// 'value' is the state value that we have transitioned FROM :
Console.WriteLine("\tEnter :\t{0} -- {1} -> {2}", value, info, this);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
public override string ToString() { return (IsConstant ? Moniker : Value.ToString()); }
}
public static void Run()
{
Console.Clear();
// Create a signal source instance (here, a.k.a. "remote control") that implements
// IObservable<TvOperation> and IObservable<KeyValuePair<TvOperation, DateTime>> :
var remote = new SignalSource<TvOperation, DateTime>();
// Create a television state machine instance (automatically set in a default start state),
// and make it subscribe to a compatible signal source, such as the remote control, precisely :
var tv = new Television().Using(remote);
bool done;
// Always holds, assuming the call to Using(...) didn't throw an exception (in case of subscription failure) :
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(tv != null, "There's a bug somewhere: this message should never be displayed!");
// As commonly done, we can trigger a transition directly on the state machine :
tv.MoveNext(TvOperation.Plug, DateTime.Now);
// Alternatively, we can also trigger transitions by emitting from the signal source / remote control
// that the state machine subscribed to / is an observer of :
remote.Emit(TvOperation.SwitchOn, DateTime.Now);
remote.Emit(TvOperation.SwitchOff);
remote.Emit(TvOperation.SwitchOn);
remote.Emit(TvOperation.SwitchOff, DateTime.Now);
done =
(
tv.
MoveNext(TvOperation.Unplug).
MoveNext(TvOperation.Dispose) // MoveNext(...) returns null iff tv.IsFinal == true
== null
);
remote.Emit(TvOperation.Unplug); // Ignored by the state machine thanks to the OnComplete(...) override above
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Is the TV's state '{0}' a final state? {1}", tv.Value, done);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Note : this example is rather artificial and mostly meant to demo a number of orthogonal features. There should seldomly be a real need to implement the state value domain itself by a full blown class, using the CRTP ( see : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Curiously_recurring_template_pattern ) like this.
Here's for a certainly simpler and likely much more common implementation use case (using a simple enum type as the states value domain), for the same state machine, and with the same test case :
https://code.google.com/p/ysharp/source/browse/trunk/StateMachinesPoC/WatchingTVSample.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Test
{
using Machines;
public static class WatchingTvSample
{
public enum Status { Unplugged, Off, On, Disposed }
public class DeviceTransitionAttribute : TransitionAttribute
{
public Status From { get; set; }
public string When { get; set; }
public Status Goto { get; set; }
public object With { get; set; }
}
// State<Status> is a shortcut for / derived from State<Status, string>,
// which in turn is a shortcut for / derived from State<Status, string, object> :
public class Device : State<Status>
{
// Executed before and after every state transition :
protected override void OnChange(ExecutionStep step, Status value, string info, object args)
{
if (step == ExecutionStep.EnterState)
{
// 'value' is the state value that we have transitioned FROM :
Console.WriteLine("\t{0} -- {1} -> {2}", value, info, this);
}
}
public override string ToString() { return Value.ToString(); }
}
// Since 'Device' has no state graph of its own, define one for derived 'Television' :
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.Unplugged, When = "Plug", Goto = Status.Off)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.Unplugged, When = "Dispose", Goto = Status.Disposed)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.Off, When = "Switch On", Goto = Status.On)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.Off, When = "Unplug", Goto = Status.Unplugged)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.Off, When = "Dispose", Goto = Status.Disposed)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.On, When = "Switch Off", Goto = Status.Off)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.On, When = "Unplug", Goto = Status.Unplugged)]
[DeviceTransition(From = Status.On, When = "Dispose", Goto = Status.Disposed)]
public class Television : Device { }
public static void Run()
{
Console.Clear();
// Create a television state machine instance, and return it, set in some start state :
var tv = new Television().Start(Status.Unplugged);
bool done;
// Holds iff the chosen start state isn't a final state :
System.Diagnostics.Debug.Assert(tv != null, "The chosen start state is a final state!");
// Trigger some state transitions with no arguments
// ('args' is ignored by this state machine's OnChange(...), anyway) :
done =
(
tv.
MoveNext("Plug").
MoveNext("Switch On").
MoveNext("Switch Off").
MoveNext("Switch On").
MoveNext("Switch Off").
MoveNext("Unplug").
MoveNext("Dispose") // MoveNext(...) returns null iff tv.IsFinal == true
== null
);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Is the TV's state '{0}' a final state? {1}", tv.Value, done);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Press any key...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
'HTH