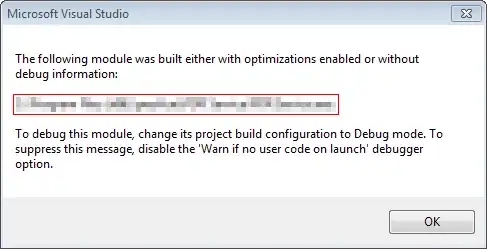
Please don't close this question. It is not related to question What does it mean to "program to an interface"?
I am trying to learn ExecutorService interface and its methods. I created an object of type ExecutorService using Executors class static method newFixedThreadPool() and trying to call the execute() method of ExecutorService interface.
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
class WorkerThread implements Runnable {
private String message;
public WorkerThread(String s) {
this.message = s;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " (Start) message = " + message);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " (End)");// prints thread name
}
}
public class TestThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);// creating a pool of 5 threads
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Runnable worker = new WorkerThread("" + i);
executor.execute(worker);// calling execute method of ExecutorService
}
executor.shutdown();
while (!executor.isTerminated()) {
}
System.out.println("Finished all threads");
}
}
In above code, I have created an object of type ExecutorService using Executors class newFixedThreadPool method which creates a pool of 5 threads.
But How executor is calling execute() method here, as it is an abstract method of ExecutorService interface and the Executors class also don't have any execute() method?