according to this article, WCF with named pipes is the best choice for IPC, and it is around 25 % faster than .Net Remoting.
I have the following code that compares WCF with named pipes with .Net Remoting:
[ServiceContract]
internal interface IRemote
{
[OperationContract]
string Hello(string name);
}
[ServiceBehavior]
internal class Remote : MarshalByRefObject, IRemote
{
public string Hello(string name)
{
return string.Format("Hello, {0}!", name);
}
}
class Program
{
private const int Iterations = 5000;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestWcf(Iterations);
TestRemoting(Iterations);
TestWcf(Iterations);
TestRemoting(Iterations);
TestWcf(Iterations);
TestRemoting(Iterations);
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void TestRemoting(int iterations)
{
var domain = AppDomain.CreateDomain("TestDomain");
var proxy =
(IRemote)
domain.CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().Location, "ConsoleApplication6.Remote");
Console.WriteLine("Remoting: {0} ms.", Test(proxy, iterations));
}
private static void TestWcf(int iterations)
{
var address = "net.pipe://localhost/test";
var host = new ServiceHost(typeof (Remote));
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof (IRemote), new NetNamedPipeBinding(), address);
host.Open();
var proxy = ChannelFactory<IRemote>.CreateChannel(new NetNamedPipeBinding(), new EndpointAddress(address));
Console.WriteLine("Wcf: {0} ms.", Test(proxy, iterations));
host.Close();
}
private static double Test(IRemote proxy, int iterations)
{
var start = DateTime.Now;
for (var i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
proxy.Hello("Sergey");
}
var stop = DateTime.Now;
return (stop - start).TotalMilliseconds;
}
}
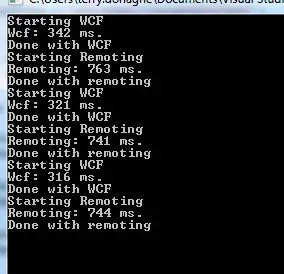
A got the following results for 5000 iterations:
Wcf: 14143 ms.
Remoting: 2232 ms.
Wcf: 14289 ms.
Remoting: 2130 ms.
Wcf: 14126 ms.
Remoting: 2112 ms.
Wcf is around 7 times slower than .Net Remoting in this test.
I tried to:
- set the security mode to None;
- set the InstanceContextMode to Single/PerCall;
- set the ConcurrencyMode to Single/Multiple;
but the results are the same.
Does anybody know what I do wrong? Why WCF is so slow?
Is there a way to speed up this code?
Thanks in advance.
EDIT:
I have modified the test a little bit. The contract is the same.
The first test looks like this (Wcf test):
class Program
{
private const int Iterations = 5000;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var address = "net.pipe://localhost/test";
var host = new ServiceHost(typeof(Remote));
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IRemote), new NetNamedPipeBinding(NetNamedPipeSecurityMode.None), address);
host.Open();
var proxy = ChannelFactory<IRemote>.CreateChannel(new NetNamedPipeBinding(NetNamedPipeSecurityMode.None), new EndpointAddress(address));
TestWcf(proxy, Iterations);
TestWcf(proxy, Iterations);
TestWcf(proxy, Iterations);
TestWcf(proxy, Iterations);
TestWcf(proxy, Iterations);
Console.ReadKey();
host.Close();
}
private static void TestWcf(IRemote proxy, int iterations)
{
var start = DateTime.Now;
for (var i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
proxy.Hello("Sergey");
}
var stop = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("Wcf: {0} ms.", (stop - start).TotalMilliseconds);
}
}
Here are the results:
Wcf: 2564 ms.
Wcf: 1026 ms.
Wcf: 986 ms.
Wcf: 990 ms.
Wcf: 992 ms.
The second test looks like this (.Net Remoting test):
class Program
{
private const int Iterations = 5000;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var domain = AppDomain.CreateDomain("TestDomain");
var proxy =
(IRemote)
domain.CreateInstanceFromAndUnwrap(Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().Location, "ConsoleApplication6.Remote");
TestRemoting(proxy, Iterations);
TestRemoting(proxy, Iterations);
TestRemoting(proxy, Iterations);
TestRemoting(proxy, Iterations);
TestRemoting(proxy, Iterations);
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void TestRemoting(IRemote proxy, int iterations)
{
var start = DateTime.Now;
for (var i = 0; i < iterations; i++)
{
proxy.Hello("Sergey");
}
var stop = DateTime.Now;
Console.WriteLine("Remoting: {0} ms.", (stop - start).TotalMilliseconds);
}
}
Here are the results:
Remoting: 261 ms.
Remoting: 224 ms.
Remoting: 252 ms.
Remoting: 243 ms.
Remoting: 234 ms.
As you can see, .Net Remoting is faster again. The tests were ran outside the debugger.
Why is this so?