Back in the Windows 7 days, Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool was unable to scan RAM beyond 4GB:
...the tool can address only up to 4GB of RAM and will not scan beyond that range.
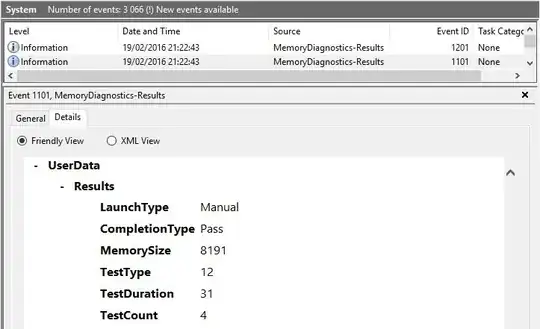
Fast-forward to today. Windows 10 has, built in, a (presumably) later version of the Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool tool. I am running it now on a PC with 16GB RAM. But the GUI is extremely plain. It does not show what amount or range of RAM it's scanning.
Does anyone know if this latest Windows 10 incarnation of the tool scans all 16GB of RAM, or is it still limited to the first 4GB like previous versions?
Extra info for the extra curious:
Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool does not run under Windows. It is a bare-metal app that has direct access to physical RAM (well, almost direct, but no need to get too technical). Without being privy to the source code, we can only speculate how it runs under the hood and why there was/is a 4GB limit. Clearly even 32-bit bare-metal apps can gain access to physical RAM above 4GB, so long as such apps utilize protected mode together with PAE. That's exactly how Memtest86 used to do it, before native 64-bit support was introduced.*
Ultimately, this question is not about what is possible and how, but what Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool is capable of. Is the latest version that ships with Windows 10 still limited to the first 4GB of RAM?