A concise summary can be found on Wikipedia:
Legal characters for DOS filenames include the following:
- Upper case letters
A–Z
- Numbers
0–9
- Space (though trailing spaces in either the base name or the extension are considered to be padding and not a part of the filename, also filenames with spaces in them must be enclosed in quotes to be used on a DOS command line, and if the DOS command is built programmatically, the filename must be enclosed in quadruple quotes when viewed as a variable within the program building the DOS command.)
! # $ % & ' ( ) - @ ^ _ ` { } ~- Values 128–255 (though if NLS services are active in DOS, some characters interpreted as lowercase are invalid and unavailable)
This excludes the following ASCII characters:
" * + , / : ; < = > ? \ [ ] | [9]- Windows/MS-DOS has no shell escape character
. (U+002E . full stop) within name and extension fields, except in . and .. entries (see below)- Lower case letters
a–z (stored as A–Z on FAT12/FAT16)
- Control characters 0–31
- Value 127 (DEL)[dubious – discuss]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/8.3_filename#Directory_table
And here's what MS-DOS 6 user guide officially said
Naming Files and Directories
Every file and directory, except for the root directory on each drive, must have a name. The following list summarizes the rules for naming files and directories. File and directory names:
- Can be up to eight characters long. In addition, you can include an extension up to three characters long.
- Are not case-sensitive. It does not matter whether you use uppercase or lowercase letters when you type them.
- Can contain only the letters A through Z, the numbers 0 through 9, and the following special characters: underscore (
_), caret (^), dollar sign ($), tilde (~), exclamation point (!), number sign (#), percent sign (%), ampersand (&), hyphen (-), braces ({}), at sign (@), single quotation mark (`), apostrophe ('), and parentheses (). No other special characters are acceptable.
- Cannot contain spaces, commas, backslashes, or periods (except the period that separates the name from the extension).
- Cannot be identical to the name of another file or subdirectory in the same directory.
This is from PC-DOS 7:
The name you assign to a file must meet the following criteria:
- It can contain no more than eight characters.
It can consist of the letters A through Z, the numbers 0 through 9, and the following special characters:
_ underscore ^ caret
$ dollar sign ~ tilde
! exclamation point # number sign
% percent sign & ampersand
- hyphen {} braces
@ at sign ` single quote
' apostrophe () parentheses
Note: No other special characters are acceptable.
- The name cannot contain spaces, commas, backslashes, or periods (except the period that separates the name from the extension).
- The name cannot be one of the following reserved file names: CLOCK$, CON, AUX, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, LPT4, NUL, and PRN.
- It cannot be the same name as another file within the directory.
User's Guide - PC DOS 7
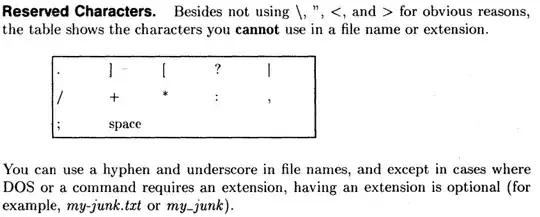
The first byte of a name must not be 0x20 (space). Short names or extensions are padded with spaces. Special ASCII characters 0x22 ("), 0x2a (*), 0x2b (+), 0x2c (,), 0x2e (.), 0x2f (/), 0x3a (:), 0x3b (;), 0x3c (<), 0x3d (=), 0x3e (>), 0x3f (?), 0x5b ([), 0x5c (\), 0x5d (]), 0x7c (|) are not allowed.
The FAT filesystem
If you're also interested in MS-DOS 5.0 then here it is.