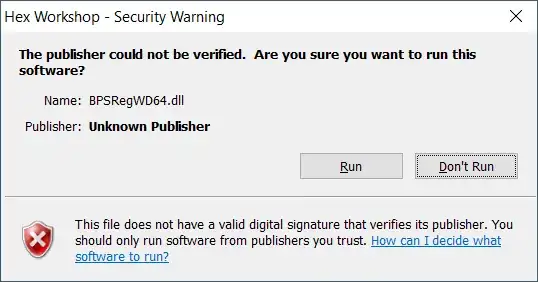
One of my .dll files is unsigned, and every single time I run the program that uses it, it pops up with this warning:
I've tried to edit the following registry key to include both .exe and .dll files HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Associations\LowRiskFileTypes, but it still gives me the warning. How can I get rid of this? I don't mind if I have to disable the warning globally or anything, I'm just sick of seeing it. And to be clear, this file is not on a network share or anything--it's just on my hard drive.
I'm running the latest build (not Insider) of Windows 10 Home by the way.