I have an HP laptop which I charge with a USB-C charger through the USB-C port. I have no idea which power delivery (PD) version it has and if it's PD-compliant at all. However, as the charging works, he-he, I assume it is.
On the HP website reference page about power delivery I read this:
Some 2015 or newer HP commercial notebooks can draw power from an external device such as an AC adapter, at different input voltages such as 5V, 9V, 10V, 12V, 15V, and 20V voltages. Not all voltages are supported on all models.
And the same voltages I recognize on my Baseus EU910 charger:
DC 5V/3A, 9V/3A, 12V/3A, 15V/3A, 20V/3A, (60W max)
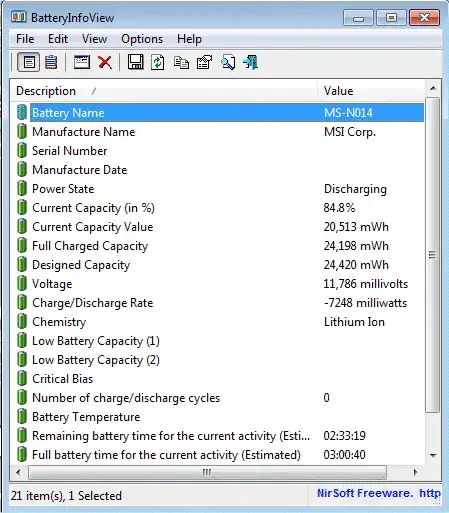
Can one check which voltage is used by the charger or consumer at the moment?
I inspected other questions on this topic: 1, 2, 3, but none of them exactly addresses my question.
I am aware that some kind of negotiation is held between the PD provider and the PD consumer, when they decide which voltage they will use for the current session. For me, it looks like pretty possible to get this information with some AIDA64-alike tool or programmatically via WMIC, etc. Is it?