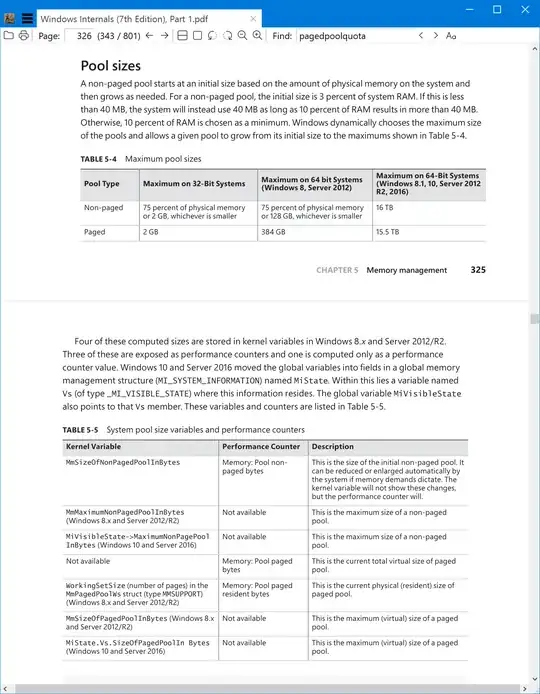
I'd like to battle paged pool memory leak caused by audio driver. I came up with the idea to limit the paged pool memory size to a reasonable amount. In "Windows Internals, Part 1" book by SysInternals on page 363 I found out about Memory Management Registry Keys. However the article states keys described — including PagedPoolLimit — are for 32-bit operating systems only.
Is there any other way I can manage this in 64-bit Windows 10? Or maybe that's a bad idea altogether.
Here's extraction from the book in case I misunderstand something:
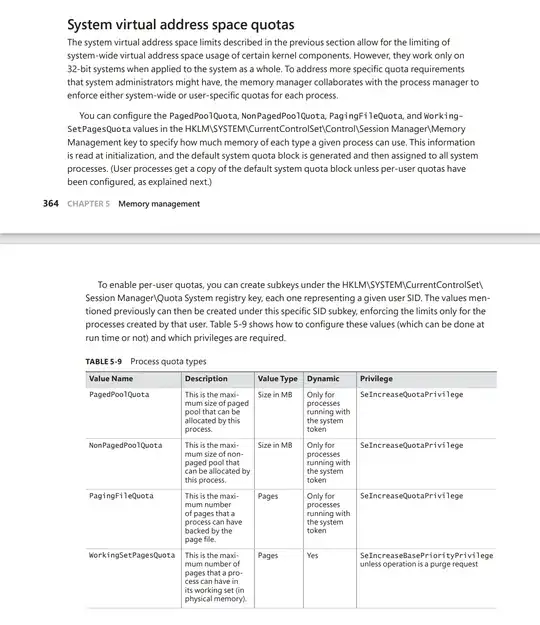
And here's an article by IBM that doesn't mention 32-bit-only compatibility.
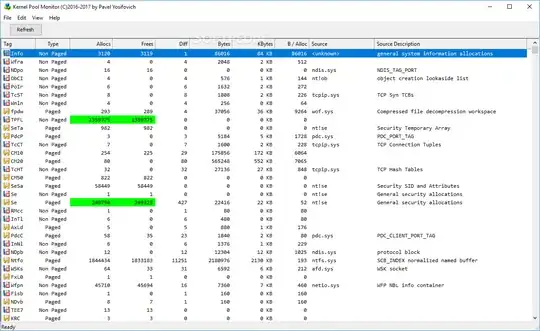
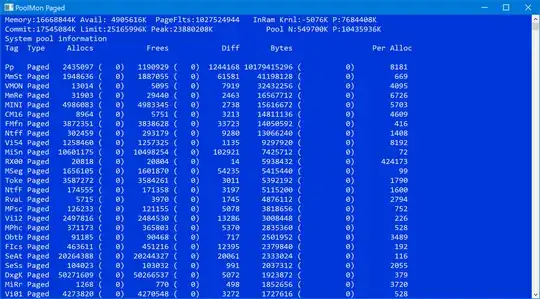
P.S. Here's what my paged pool memory leak looks like after a week of uptime (I'm 100% sure it's audio driver since I did my troubleshooting via PoolMon of WDK and Windows Performance Analyzer of Windows SDK as briely described in this answer and in SysInternals book):
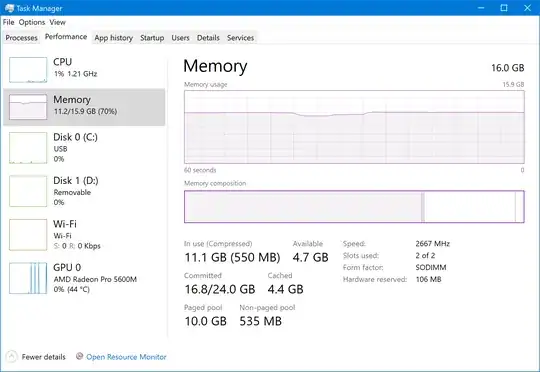
Update In Windows Internals (7th edition) at page 384 it is stated that maximum paged pool size for 64-bit Windows 10 is 15.5 TB. It provides explanation where this size is set. But I have no idea how to change this (i.e. to 5 or 10% of physical RAM). Here's an extraction from the book:
Four of these computed sizes are stored in kernel variables in Windows 8.x and Server 2012/R2. Three of these are exposed as performance counters and one is computed only as a performance counter value. Windows 10 and Server 2016 moved the global variables into fields in a global memory management structure (MI_SYSTEM_INFORMATION) named MiState. Within this lies a variable named Vs (of type _MI_VISIBLE_STATE) where this information resides. The global variable MiVisibleState also points to that Vs member. These variables and counters are listed in Table 5-5.