I would like to change the prompt to $p$g$_$f permanently, but it resets itself every time I reopen the command window.
How can I get it to stay the same forever?
I would like to change the prompt to $p$g$_$f permanently, but it resets itself every time I reopen the command window.
How can I get it to stay the same forever?
At the command prompt type:
setx Prompt $p$g$_$fThen reopen the command prompt.
For anyone that doesn't know how to get help for DOS/CMD commands, type:
setx /?
To get:
SetX has three ways of working:
Syntax 1:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]] var value [/M]
Syntax 2:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]] var /K regpath [/M]
Syntax 3:
SETX [/S system [/U [domain\]user [/P [password]]]]
/F file {var {/A x,y | /R x,y string}[/M] | /X} [/D delimiters]
Description:
Creates or modifies environment variables in the user or system
environment. Can set variables based on arguments, regkeys or
file input.
Parameter List:
/S system Specifies the remote system to connect to.
/U [domain\]user Specifies the user context under which
the command should execute.
/P [password] Specifies the password for the given
user context. Prompts for input if omitted.
var Specifies the environment variable to set.
value Specifies a value to be assigned to the
environment variable.
/K regpath Specifies that the variable is set based
on information from a registry key.
Path should be specified in the format of
hive\key\...\value. For example,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\
Control\TimeZoneInformation\StandardName.
/F file Specifies the filename of the text file
to use.
/A x,y Specifies absolute file coordinates
(line X, item Y) as parameters to search
within the file.
/R x,y string Specifies relative file coordinates with
respect to "string" as the search parameters.
/M Specifies that the variable should be set in
the system wide (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)
environment. The default is to set the
variable under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER
environment.
/X Displays file contents with x,y coordinates.
/D delimiters Specifies additional delimiters such as ","
or "\". The built-in delimiters are space,
tab, carriage return, and linefeed. Any
ASCII character can be used as an additional
delimiter. The maximum number of delimiters,
including the built-in delimiters, is 15.
/? Displays this help message.
NOTE: 1) SETX writes variables to the master environment in the registry.
2) On a local system, variables created or modified by this tool
will be available in future command windows but not in the
current CMD.exe command window.
3) On a remote system, variables created or modified by this tool
will be available at the next logon session.
4) The valid Registry Key data types are REG_DWORD, REG_EXPAND_SZ,
REG_SZ, REG_MULTI_SZ.
5) Supported hives: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM),
HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU).
6) Delimiters are case sensitive.
7) REG_DWORD values are extracted from the registry in decimal
format.
Examples:
SETX MACHINE COMPAQ
SETX MACHINE "COMPAQ COMPUTER" /M
SETX MYPATH "%PATH%"
SETX MYPATH ~PATH~
SETX /S system /U user /P password MACHINE COMPAQ
SETX /S system /U user /P password MYPATH ^%PATH^%
SETX TZONE /K HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\
Control\TimeZoneInformation\StandardName
SETX BUILD /K "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows
NT\CurrentVersion\CurrentBuildNumber" /M
SETX /S system /U user /P password TZONE /K HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\
System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TimeZoneInformation\
StandardName
SETX /S system /U user /P password BUILD /K
"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\
CurrentVersion\CurrentBuildNumber" /M
SETX /F ipconfig.out /X
SETX IPADDR /F ipconfig.out /A 5,11
SETX OCTET1 /F ipconfig.out /A 5,3 /D "#$*."
SETX IPGATEWAY /F ipconfig.out /R 0,7 Gateway
SETX /S system /U user /P password /F c:\ipconfig.out /X
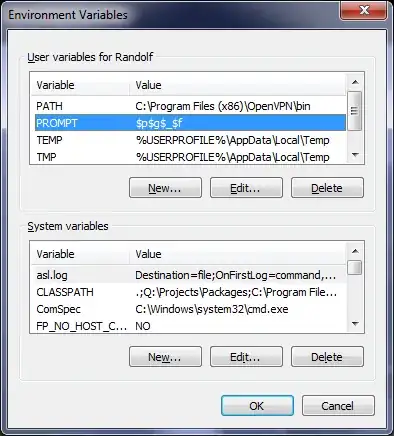
Create a new environment variable called PROMPT. Set the variable value to the desired prompt.
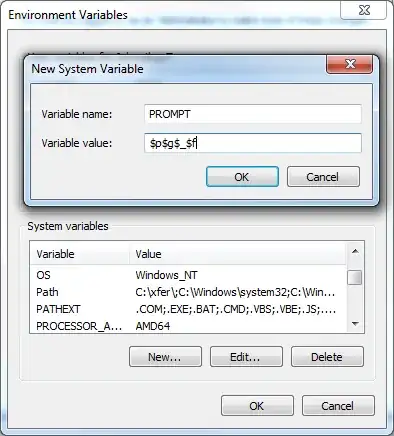
To change the appearance of your DOS Prompt (or "Command Prompt"), right-click on "Computer" (usually on your Windows Desktop or in the Windows Start Menu), then follow these steps:
This change will also survive reboots.


Windows comes with Windows PowerShell which allows pipelining among other former Linux-only features.
You can start it by clicking the Start button and entering PowerShell, which gives you three options. Click PowerShell. Right click on the window title bar and select Properties. In the opening window you configure view and behavior settings.
Otherwise instead of opening PowerShell in the first place select and click PowerShell modules.
See the Microsoft documentation for what you can do:
PS: I wouldn't recommend the classic shell if you develop console applications.
Definitive method:
setx prompt ""
For all users:
setx prompt "" /M
Example of prompt customizable, with style:
setx PROMPT "$_$e[0;1;44mN$e[1;30;47mI$e[0;1;44mC$E[35;40m $d$s$t$h$h$h$h$h$h$_$E[1;33;40m$p$_$E[0;0m~$g$s"