At the end of the page you have linked to, you have links to articles explaining how to use the URL Rewrite Module.
Generally, you would need to install the URL Rewrite Module into IIS, then configure one or more rewrite rules using either IIS Manager or by manually editing web.config files.
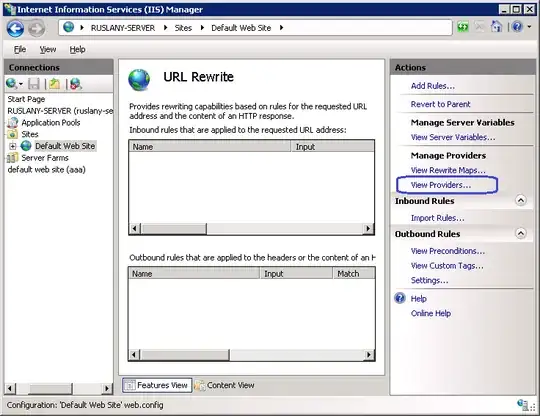
1. Locate and Open the URL Rewrite UI within IIS Manager

2. You can manage inbound and outbound rewrite rules
3. Here is a simple example of a regex match and rewrite to a subweb
4. The resulting rewrite rules created in web.config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<rewrite>
<rules>
<rule name="MyRule001" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="^services/(.*)" />
<action type="Rewrite" url="http://localhost/my/services/{R:1}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
This is enough to rewrite most URLs. It's not necessary to configure any providers in 99.999% of most real-world scenarios. They exist only for advanced rewriting needs (dynamic rewriting, for example, rather than a static rule.)
It's primarily intended by Microsoft that you simply define rewrite rules that meet your needs as shown above.
Hope this helps others.