If you have two available computers, you can measure the TCP speed directly
between them, without using file-transfer which is notoriously slow.
The tool to use is iPerf, available for all major operating
systems.
For details see the article
How to use Iperf to test the speed on TP-Link routers.
The schema of test configuration is:
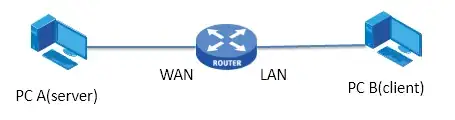
Use your computer as the server connected via Wifi.
Both computers should be on the LAN side of the router.
You may connect the computer you are not testing to the router by cable (if faster),
to ensure that its performance is not the bottleneck in the test.
The main points are:
Install iPerf on both computers
Disable all firewalls
Set static IP address for PC A
Set static IP address for WAN port of the Router (your router configuration
must support this)
On PC A start the server:
iperf3 -s
on PC B run the command :
iperf3 -c 192.168.2.30 (replace IP as required)
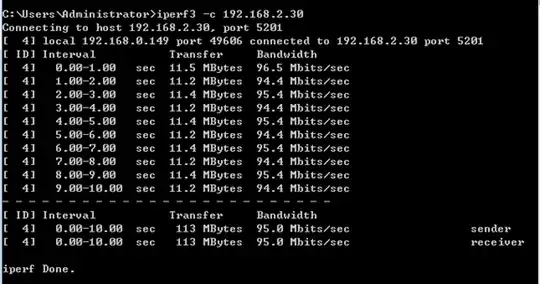
The result may look like this (on the sender) when the speed is 95 Mbps: