On Windows 11. Command Prompt can be launched from Windows Terminal.
The Screen buffer size is called "History size"
To increase, open the Windows Terminal Settings using CTRL+,
Click the Command Prompt profile tab on the left
Then under the Additional settings header click the Advanced menu
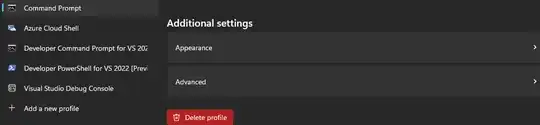
The Advanced submenu will display a History size option
(The number of lines above the ones displayed in the window you can scroll back to).
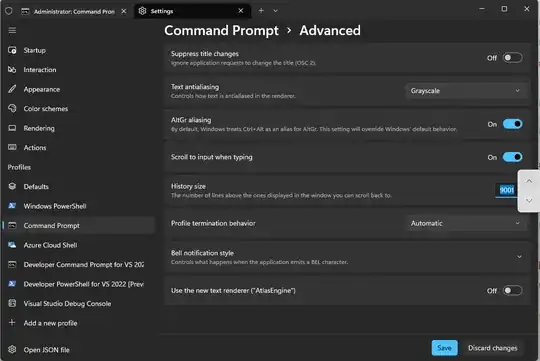
Increase the History size from the default of "9001"
The maximum supported size history size is "32767" even if you enter a number higher than this.
Click Save and restart Windows Terminal for the changes to take effect
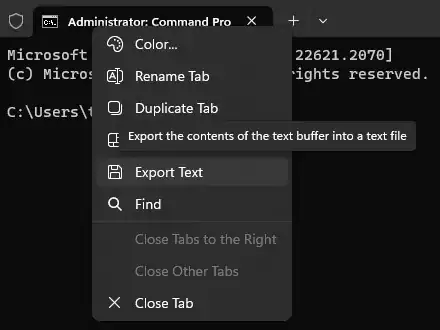
It is also possible to Save the contents of the Window buffer to file by right clicking the command tab and clicking the Export Text context menu option
References
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/terminal/customize-settings/profile-advanced


