Is there anything built in to Windows that would allow me to list all of the installed software on a computer in a fashion that can be copy/pasted to a spreadsheet? I know there is software that can do this, but I can't install anything. I'd prefer not to use a batch file if possible, but I imagine that is going to be the only way. Ideally, I would be able to output the same information as is shown on the (un-expanded) view of the Add/Remove Programs Form.
9 Answers
Fire up your console and type:
wmic product get name,version
It takes a while, but you'll get the full list of installed programs. WMIC is the console version of Windows Management Instrumentation, available from Windows 2000 and onwards. Following the instructions here and here, you can tell WMIC to output in an XML format, that might be a bit more convenient for you. However just calling wmic product get name will get you a list of application names, that you can easily copy paste to a text editor and convert to spreadsheet format.
Alternatively, enter:
wmic /output:C:\InstallList.txt product get name,version
This will output a TXT file with the list of programs. You can then paste that into a spreadsheet, if you want.
Source: http://helpdeskgeek.com/how-to/generate-a-list-of-installed-programs-in-windows/
Also you can use the csv.xsl file to format the output into a CSV list of results:
wmic /output:C:\InstallList.csv product get /format:csv.xsl
or the htable.xsl file to create an HTML table of results:
wmic /output:C:\InstallList.htm product get /format:hform.xsl
Run wmic product get to get a list of installed software, it should be exactly the same list as add/remove programs.
You can supposedly get it to to output in a specific format, but I haven't tried it.
(Use wmic product get /? to see the parameters including the output formatting, I tried to include it here but the formatting wasn't quite right.)
- 2,880
As others have mentioned, you can get this info with a WMI query for Win32_Product objects. PowerShell will even dump it to a CSV file for you if you'd like.
Get-WmiObject -Class "Win32_Product" | Export-CSV (Join-Path $home "Win32_Product.csv")
However, you should search for Win32_Product issues. It's not all gumdrops and lollipops.
- 238
- 3
- 7
- 8,752
WMIC won't work on a Server unless you have explicitly installed Management and Monitoring Tools in the Add/Remove Windows Components menu.
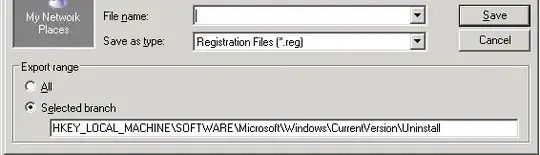
Another solution is to go to the Registry and look at all the Uninstallable Programs by going to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
You'll have to click each one individually to see the value, so instead, you can right click on the Uninstall folder and select Export. Make sure that the Export Range is set to include only the Selected Branch:
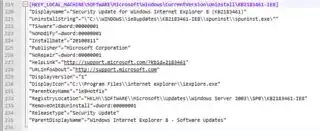
Then you can open up the .reg file in notepad++, but you're going to get a lot of extra information on each application:
You can get rid of all lines that don't start with "DisplayName" by matching against the following regex:
^(?!"DisplayName").+
Then you can remove either string "DisplayName" or " by matching on the following regex:
("DisplayName"="|")
Then you can remove any duplicates lines by matching on the following regex:
^(.*)(\r?\n\1)+$
Or you can just sort lines alphabetically and then delete the blank ones
The easiest way I found is running piriform's ccleaner.
This has a button at Tools -> Uninstall -> "save to text file"
- 67
The problem querying only the HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall key, is that you only get the 32-bit applications. 64-bit applications reside in HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall.
You can query both keys in a oneliner and output it to a .txt file as follows in PowerShell:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\*,HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate | Format-Table -AutoSize > $Profile\..\..\InstalledPrograms.txt
The resulting InstalledPrograms.txt can be found in the Documents folder.
- 191
On Windows 7 you can use a PowerShell script:
Open PowerShell by clicking Start button and typing powershell into the search field.
Then enter the following command in the PowerShell Window:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate | Format-Table –AutoSize
You can remove any of the fields: DisplayName, DisplayVersion, etc. if you don't need them.
If you want to save output to a file, use redirection:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate | Format-Table –AutoSize > C:\temp\AllInstalledPrograms.txt
- 12,326
- 413
Two other non-command-line solutions not previously mentioned are:
MyUninstaller - a freeware program from NirSoft that, besides uninstalling, can also export to HTML a comprehensive list of all installed software that includes a lot of additional info. It has the advantage of being portable. While it is not "built-in", you can run it from a USB drive. You can find it here.
Belarc Advisor - a freeware (for personal use) program that does security analysis and comprehensive inventory of your computer's hardware and software. It is available here. Unfortunately, you must install it, so it does not fully meet the OP's needs, but may meet the needs of others who have the same question and are able to install.
- 2,306
The encoded version in c# installed programs via registry
using Microsoft.Win32;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
namespace SoftwareInventory
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//!!!!! Must be launched with a domain administrator user!!!!!
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
StringBuilder sbOutFile = new StringBuilder();
Console.WriteLine("DisplayName;IdentifyingNumber");
sbOutFile.AppendLine("Machine;DisplayName;Version");
//Retrieve machine name from the file :File_In/collectionMachines.txt
//string[] lines = new string[] { "NameMachine" };
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(@"File_In/collectionMachines.txt");
foreach (var machine in lines)
{
//Retrieve the list of installed programs for each extrapolated machine name
var registry_key = @"SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall";
using (Microsoft.Win32.RegistryKey key = RegistryKey.OpenRemoteBaseKey(RegistryHive.LocalMachine, machine).OpenSubKey(registry_key))
{
foreach (string subkey_name in key.GetSubKeyNames())
{
using (RegistryKey subkey = key.OpenSubKey(subkey_name))
{
//Console.WriteLine(subkey.GetValue("DisplayName"));
//Console.WriteLine(subkey.GetValue("IdentifyingNumber"));
if (subkey.GetValue("DisplayName") != null && subkey.GetValue("DisplayName").ToString().Contains("Visual Studio"))
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0};{1};{2}", machine, subkey.GetValue("DisplayName"), subkey.GetValue("Version")));
sbOutFile.AppendLine(string.Format("{0};{1};{2}", machine, subkey.GetValue("DisplayName"), subkey.GetValue("Version")));
}
}
}
}
}
//CSV file creation
var fileOutName = string.Format(@"File_Out\{0}_{1}.csv", "Software_Inventory", DateTime.Now.ToString("yyyy_MM_dd_HH_mmssfff"));
using (var file = new System.IO.StreamWriter(fileOutName))
{
file.WriteLine(sbOutFile.ToString());
}
//Press enter to continue
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to continue !");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
- 201