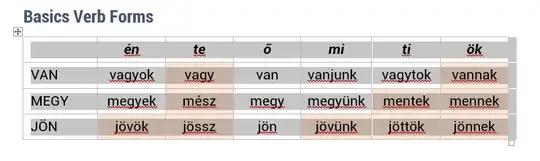
Here is a macro that works by copy-pasting each cell individually. This way it worked for me with equations in almost all cells.
I'm on Word Version 2301 (from Microsoft 365, probably whatever is the newest version in 2024). To be safe, I copy the table, paste it into a new empty document, then run the macro there.
Sub TransposeTable()
Dim tbl As Table
Dim newTbl As Table
Dim i As Long, j As Long
Dim rowCount As Long, colCount As Long
Dim rng As Range
' Get the first table in the document
Set tbl = ActiveDocument.Tables(1)
' Get the number of rows and columns
rowCount = tbl.Rows.Count
colCount = tbl.Columns.Count
' Set the range after the original table
Set rng = tbl.Range
rng.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
' Insert two new lines after the original table to avoid them sticking together
rng.InsertAfter vbCrLf & vbCrLf
rng.Collapse Direction:=wdCollapseEnd
' Add a new table with transposed dimensions at the end of the original table
Set newTbl = ActiveDocument.Tables.Add(Range:=rng, NumRows:=colCount, NumColumns:=rowCount)
' Loop through each cell in the original table and copy-paste it to the transposed table
For i = 1 To rowCount
For j = 1 To colCount
' Copy the cell content from the original table
tbl.Cell(i, j).Range.Copy
' Paste the content into the transposed table
newTbl.Cell(j, i).Range.Paste
Next j
Next i
' Optional: Delete the original table
' tbl.Delete
End Sub