I noticed that one of my drives was full after moving some files onto it:
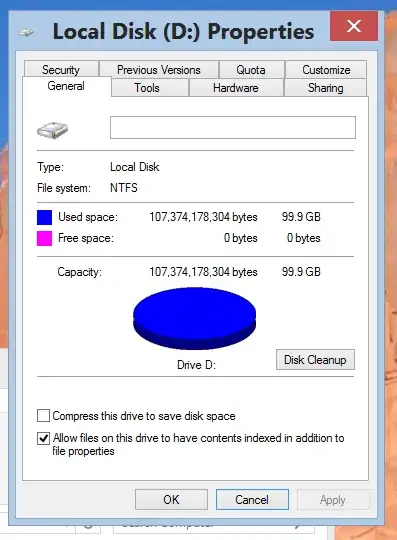
I thought it unlikely that copying files of random sizes would result in exactly filling the available space, so I became suspicious.
I then dragged a file that was 1.57 MB off the drive and onto my desktop (via shift+drag). The drive's free space then said 1.52 MB, which didn't make sense. I then clicked "Undo Move" and it would not move the file back, claiming there was not enough free space.
Can anyone make sense of this? There is nothing else being written to the drive. I'm guessing it has something to do with the internal structure of the drive (e.g. fragmentation [although it says 0% fragmented]), and this is a drive on a virtual machine.