OpenSCAD User Manual/Characters Strings
part of the section on Values, Data Types, and Constants
Characters
Characters are not an explicit type in this language, but there are some noteworthy points of implementation.
The Unicode character set is the basis for text in OpenSCAD strings.
Character literals are normally written as single element strings, like "a", but may also be converted from their ASCII code values, as "a" == chr(97).
Escape Characters
In string literals printable ASCII characters may be written as themselves:
s = "abcdefg";
To signal an "escape" from normal string processing a backslash ( "\" ) indicates to the text processor that the following character may need special treatment. When that character is not recognized as a code with special meaning the backslash is just deleted and the character is passed to the output untouched.
Control codes in the ASCII ordinal range of 00-ff (0-255) may be written in strings as single byte hexcodes following the backslash ('\x') escape code as
echo("\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x7f\x80\x81");
Limitation: only the subset \x01 to \x7f are supported

As seen in this image, ASCII (NUL), the null character, is drawn as a space (" ") and escaped codes \x80 and greater are rendered as literal text.
Multibyte Unicode literals are written as:
- \u0123 - 4 bytes (note: lowercase \u)
- \U012345 - 6 bytes (note: uppercase \U)
NULL in all its forms \x00 \u0000 \U000000 is rendered as a space (" ")
Example
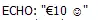
Echo ( "\u20AC10 \u263A"); will render as in this image:
Strings
String are zero or more Unicode characters enclosed in double quotes ( '"' ). A single quote ( ' ) outside of a string is a syntax error and so cannot enclose a string.
Strings are passed as arguments, or parameters, to parts of the app that have their own processing "engines" for handling text. Thus console output can show differently from text rendered text() module.
Escape Characters in Strings
As seen above with character escape codes there are ways to include special characters in a string.
To be able to use a quote or a backslash in a string literal we use these additional escapes:
- a quote "
- use \", so "quotes around \"a\" in a string"
- a slash \
- use \\, so "C:\\folder\\file.ext"
There are three additional escape codes that will be familiar to C programmers:
- tab
- "\t" jump to next tab stop
- newline
- "\n" begin following output on next line
- return
- "\r" same as newline in console
to apply basic formatting of console output, as shown here:
echo("\n\tTITLE\nunder\rover\n\t1\t2 jumps");
is rendered as:
ECHO: " TITLE under over 1 2 jumps"