To apply the accepted solution of @magicandre1981 with a copy & past PowerShell script, just execute the following from an elevated PowerShell prompt:
Function Enable-Privilege
{
param([ValidateSet("SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege", "SeAuditPrivilege", "SeBackupPrivilege",
"SeChangeNotifyPrivilege", "SeCreateGlobalPrivilege", "SeCreatePagefilePrivilege",
"SeCreatePermanentPrivilege", "SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege", "SeCreateTokenPrivilege",
"SeDebugPrivilege", "SeEnableDelegationPrivilege", "SeImpersonatePrivilege", "SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege",
"SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege", "SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege", "SeLoadDriverPrivilege",
"SeLockMemoryPrivilege", "SeMachineAccountPrivilege", "SeManageVolumePrivilege",
"SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege", "SeRelabelPrivilege", "SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege",
"SeRestorePrivilege", "SeSecurityPrivilege", "SeShutdownPrivilege", "SeSyncAgentPrivilege",
"SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege", "SeSystemProfilePrivilege", "SeSystemtimePrivilege",
"SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege", "SeTcbPrivilege", "SeTimeZonePrivilege", "SeTrustedCredManAccessPrivilege",
"SeUndockPrivilege", "SeUnsolicitedInputPrivilege")]$Privilege,
$ProcessId = $pid,
[Switch]$Disable)
$Definition = @'
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
public class AdjPriv
{
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", ExactSpelling = true, SetLastError = true)]
internal static extern bool AdjustTokenPrivileges(IntPtr htok, bool disall,
ref TokPriv1Luid newst, int len, IntPtr prev, IntPtr relen);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", ExactSpelling = true, SetLastError = true)]
internal static extern bool OpenProcessToken(IntPtr h, int acc, ref IntPtr phtok);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
internal static extern bool LookupPrivilegeValue(string host, string name, ref long pluid);
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack = 1)]
internal struct TokPriv1Luid
{
public int Count;
public long Luid;
public int Attr;
}
internal const int SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED = 0x00000002;
internal const int SE_PRIVILEGE_DISABLED = 0x00000000;
internal const int TOKEN_QUERY = 0x00000008;
internal const int TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES = 0x00000020;
public static bool EnablePrivilege(long processHandle, string privilege, bool disable)
{
bool retVal;
TokPriv1Luid tp;
IntPtr hproc = new IntPtr(processHandle);
IntPtr htok = IntPtr.Zero;
retVal = OpenProcessToken(hproc, TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, ref htok);
tp.Count = 1;
tp.Luid = 0;
if(disable)
{
tp.Attr = SE_PRIVILEGE_DISABLED;
}
else
{
tp.Attr = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;
}
retVal = LookupPrivilegeValue(null, privilege, ref tp.Luid);
retVal = AdjustTokenPrivileges(htok, false, ref tp, 0, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero);
return retVal;
}
}
'@
$processHandle = (Get-Process -id $ProcessId).Handle
$type = Add-Type $definition -PassThru
$type[0]::EnablePrivilege($processHandle, $Privilege, $Disable)
}
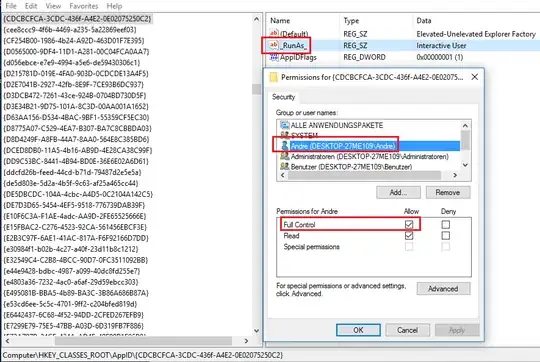
$path = 'HKLM:\Software\Classes\AppID{CDCBCFCA-3CDC-436f-A4E2-0E02075250C2}'
$acl = Get-Acl $path
$originalOwner = $acl.GetOwner([System.Security.Principal.NTAccount]).Value
$acl.SetOwner((New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount([System.Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent().Name)))
$acl | Set-Acl $path
Rename-ItemProperty -LiteralPath $path -Name "RunAs" -NewName "__RunAs";
$acl = Get-Acl $path
$acl.SetOwner((New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount($originalOwner)))
Enable-Privilege SeRestorePrivilege
$acl | Set-Acl $path
It renames the RunAs value name to __RunAs.