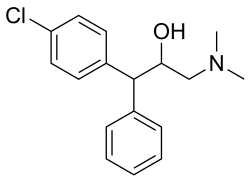
Clemeprol Other names BRL 14342
1-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-(dimethylamino)-1-phenylpropan-2-ol
CAS Number PubChem CID ChemSpider UNII ChEMBL CompTox Dashboard (EPA ) Formula C 17 H 20 Cl N O Molar mass −1 3D model (JSmol )
CN(C)CC(C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C2=CC(=CC=C2)Cl)O
InChI=InChI=1S/C17H20ClNO/c1-19(2)12-16(20)17(13-7-4-3-5-8-13)14-9-6-10-15(18)11-14/h3-11,16-17,20H,12H2,1-2H3
Key:KGSABFQIAANNPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Clemeprol is an serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) antidepressant and anticholinergic agent.[ 1]
It is an enantiomeric mixture of R and S isomers. Both isomers show similar pharmacological activity.[ 2] [ 3]
Synthesis
Published Procedure
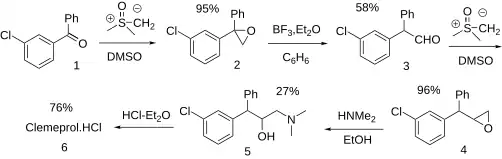
A synthetic pathway for clemeprol is disclosed: [ 4] [ 5] [ 6] [ 7] [ 8]
Clemeprol synthesis The Johnson–Corey–Chaykovsky reaction (CCR) between 3-chlorobenzophenone [1016-78-0] (1 ) and dimethylsulfoxonium methylide (aka Corey's reagent or Corey-Chaykovsky Reagent) [5367-24-8], gives 2-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-phenyloxirane [71827-53-7] (2 ). Further reaction with boron trifluoride etherate [109-63-7] gives m-chlorophenyl-phenylacetaldehyde, PC12549135 (3 ). A second Corey-Chaykovsky epoxidation gives 2-[(3-chlorophenyl)-phenylmethyl]oxirane, PC12549073 (4 ). Quenching with dimethylamine completes the synthesis of clemeprol (5 ).
Hypothetical Synthesis
A hypothetical synthesis of clemeprol based on method A in the cited literature is disclosed.[ 4]
Clemeprol synthesis (hypothetical) The precursor is called 2-(3-Chlorophenyl)-2-phenylacetonitrile (1 ). This would be prepared using methodology that was described already under the diphenylacetonitrile document. A Grignard reaction with one equivalent of methylmagnesium bromide leads to a FGI of the nitrile to the acetyl compound (2 ). The alpha-bromination of the acetyl group with one equivalent of a halogenating agent (either molecular bromine /HOAc or NBS can be used) gives (3 ). The bromide leaving group is displaced by dimethylamine giving (4 ). Sodium borohydride can then be used as the reducing agent to convert the keto carbonyl group into a secondary alcohol, completing the synthesis of clemeprol (5 ).
See also
References
^ Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents By C.R. Ganellin, David J. Triggle.
^ Clark MS, Johnson AM, McClelland GR, Nelson DR (December 1980). "Pharmacological and biochemical properties of BRL 14342, a novel potential antidepressant drug". Neuropharmacology . 19 (12): 1207– 8. doi :10.1016/0028-3908(80)90203-8 . PMID 7442949 . ^ Koch, H., Drugs Future, 1983,8, 194.
^ a b Clark JA, Clark MS, Gardner DV, Gaster LM, Hadley MS, Miller D, et al. (November 1979). "Substituted 3-amino-1,1-diaryl-2-propanols as potential antidepressant agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry . 22 (11): 1373– 9. doi :10.1021/jm00197a018 . PMID 533885 . ^ Anon., GB1448437 (1976-09-08 to Beecham Group Ltd).
^ Judith Ann Clark, U.S. patent 4,101,676 U.S. patent 4,113,972
^ Judith Ann Clark, U.S. patent 4,056,630
^ CA1049530 idem Judith Ann Clark, U.S. patent 4,028,415
SSRIs Tooltip Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SNRIs Tooltip Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors NRIs Tooltip Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors NDRIs Tooltip Norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitors NaSSAs Tooltip Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants SARIs Tooltip Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors SMS Tooltip Serotonin modulator and stimulators Others
TCAs Tooltip Tricyclic antidepressants TeCAs Tooltip Tetracyclic antidepressants Others
Non-selective MAOA Tooltip Monoamine oxidase A -selectiveMAOB Tooltip Monoamine oxidase B -selective
5-HT1A R Tooltip 5-HT1A receptor agonists GABAA R Tooltip GABAA receptor PAMs Tooltip positive allosteric modulators Gabapentinoids (α2 δ VDCC blockers ) Antidepressants Sympatholytics (Antiadrenergics )
Alpha-1 blockers (e.g., prazosin )Alpha-2 agonists (e.g., clonidine , dexmedetomidine , guanfacine )Beta blockers (e.g., propranolol , atenolol , betaxolol , nadolol , oxprenolol , pindolol ) Others
Monoaminergics Ion channel blockers
Anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin , pregabalin , mirogabalin , carbamazepine , oxcarbazepine , lacosamide , lamotrigine )Local anesthetics (e.g., lidocaine )Mexiletine TCAs Tooltip Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline , nortriptyline , desipramine )Ziconotide Others
Alpha lipoic acid Benfotiamine Botulinum toxin A Bupropion Cannabinoids (e.g., cannabis , dronabinol , nabilone )NMDA receptor antagonists (e.g., ketamine , dextromethorphan , methadone )Opioids (e.g., hydrocodone , morphine , oxycodone , methadone , buprenorphine , tramadol , tapentadol )Sodium oxybate (GHB )
DAT Tooltip Dopamine transporter (DRIs Tooltip Dopamine reuptake inhibitors )
NET Tooltip Norepinephrine transporter (NRIs Tooltip Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors )
Others: Antihistamines (e.g., brompheniramine , chlorphenamine , pheniramine , tripelennamine )Antipsychotics (e.g., loxapine , ziprasidone )Arylcyclohexylamines (e.g., ketamine , phencyclidine )Dopexamine Ephenidine Ginkgo biloba Indeloxazine Nefazodone Opioids (e.g., desmetramadol , methadone , pethidine (meperidine) , tapentadol , tramadol , levorphanol )
SERT Tooltip Serotonin transporter (SRIs Tooltip Serotonin reuptake inhibitors )
Others: A-80426Amoxapine Antihistamines (e.g., brompheniramine , chlorphenamine , dimenhydrinate , diphenhydramine , mepyramine (pyrilamine) , pheniramine , tripelennamine )Antipsychotics (e.g., loxapine , ziprasidone )Arylcyclohexylamines (e.g., 3-MeO-PCP , esketamine , ketamine , methoxetamine , phencyclidine )Cyclobenzaprine Delucemine Dextromethorphan Dextrorphan Efavirenz Hypidone Medifoxamine Mesembrine Mifepristone MIN-117 (WF-516) N-Me-5-HT Opioids (e.g., dextropropoxyphene , methadone , pethidine (meperidine) , levorphanol , tapentadol , tramadol )Roxindole
VMATs Tooltip Vesicular monoamine transporters Others See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine releasing agents • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins
.svg.png)